Substation (TSA) is a device that transmits energy or electrical signals around the direction between electrical circuits through the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. The TSA is also the place where transformers and other power distribution equipment are located, to create a complete power transmission system to supply electricity.
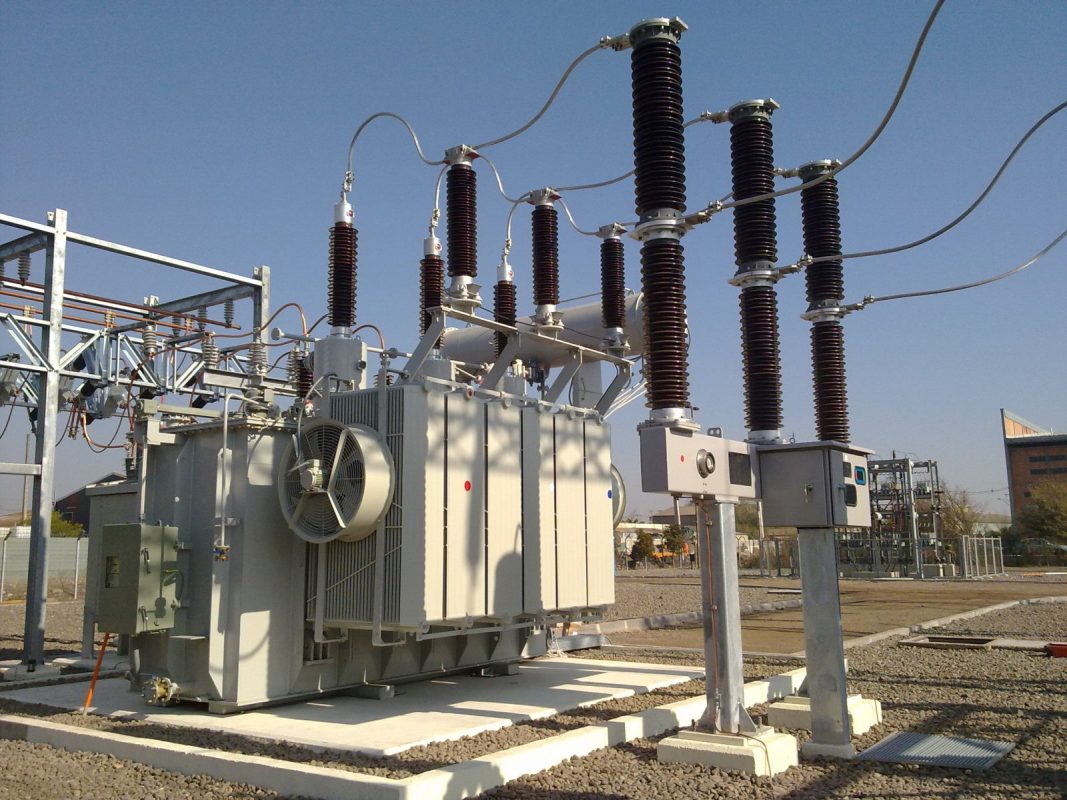

Currently there are many different types of transformers, but they all have the same structural characteristics such as: Transformer, busbar system, isolator, lightning protection system, self-contained electrical system, operating area, distribution area.
– Transformer
– Terminal equipment: there will be electric cables, terminals, etc.
– Medium voltage compartment: switching devices, transformer overload protection, devices such as medium voltage cabinets, etc.
– Low voltage compartment: low voltage cables, grounding systems, main circuit breakers, protective switching devices, etc., other auxiliary equipment (indicator lights, lightning arresters, meters, fuses, etc.)
To have a transformer station operate stably and safely, the design requirements are as follows:
+ Ensure power quality: the location of the station and the load center should be located at the load center to save power lines, and minimize power grid loss and voltage drop.
+ Ensure no investment costs are wasted.
+ Ensure safety for equipment and people: the location of the transformer station should not affect houses, factories or other structures. In addition, it is necessary to ensure industrial aesthetics near the power grid and ensure the safety corridor of the power line.
+ Have a convenient design for operation and repair.
The location of the station, the design, construction, use and operation unit of the transformer station must also fully comply with the State's regulations, including: Consolidated Document 10/VBHN-BCT of 2020 consolidating the Decree guiding the Electricity Law and the amended Electricity Law; Law No. 24/2012/QH13 dated November 20, 2012 of the National Assembly amending and supplementing a number of articles of the Electricity Law; Electricity Law No. 28/2004/QH11; Decree 14/2014/ND-CP guiding the Electricity Law on electrical safety; ... and decrees, circulars of Government agencies, other documents issued by the People's Committees of provinces/cities.
+ Priority should be given to placing near the power source or consuming device
+ Due to the continuity of use as well as the input and output voltage levels, for the type of station serving transmission work, the location of the station needs to be open, far from residential areas, cool, to reduce power loss, increase the life of the machine and other equipment in the station.
+ Place on flat ground, high position to avoid waterlogging
+ Design and construction of drainage system in and around the transformer station area must be synchronized with the station infrastructure.
+ Location must ensure convenient use, operation and repair.
Location of the station
Place the station in a place with convenient traffic because there are many electrical devices, transformers have a very large weight, avoid placing it in a place that is difficult to access.
Air where the station is located
Air contains a lot of metal dust, ... will make the switching operation easy to cause electric discharge, dangerous for the operator, reduce the life of the transformer. Therefore, the factory in the industrial park, ... should be located far from the production area with a filter system to limit dust impact on the station.
+ We can see that transformers are used everywhere, from household transformers used in electric fans to transformers used for voltage stabilization or used in electronic main boards, etc. One of the common applications is in electricity: Power transformer stations increase and decrease voltage in power transmission.
+ From small transformers (air-cooled dry transformers, currently manufactured with a capacity of over 2000 KVA), to larger transformers with coils immersed in oil (oil for insulation and heat dissipation to the steel sheets around the machine).
+ To transmit large amounts of electricity from the production site to the consumption site, the optimal solution is to increase the voltage to limit power loss and reduce the cost of investing in the transmission line.
+ The larger the amount of transmitted power, the higher the voltage.
Voltage: People divide it into 4 voltage levels:
+ Ultra High Voltage: Greater than 500 KV
+ High Voltage: 66kV, 110kV, 220kV and 500kV
+ Medium Voltage: 6kV, 10kV, 15kV, 22kV and 35 kV
+ Low Voltage: 0.4kV and 0.2kV and Voltages less than 1 KV.
According to the above classification, we have 2 names of transformer stations:
+ Intermediate Transformer Station: Receives voltage from 220 KV – 35 KV and converts it to output voltage of 35 KV – 15 KV according to usage needs.
+ Workshop Transformer Station or Distribution Transformer Station: Receives voltage of 35 KV – 6 KV and converts it to output voltage of 0.4 KV – 0.22 KV => this is the transformer station used in the low voltage network of civil buildings, commonly seen as a 22/0.4 KV station.
+ Outdoor stations are suitable for large capacity intermediate stations. Because transformers and distribution equipment are large in size, there is enough space to install these devices, saving a lot of construction costs.
+ Including stations: Integrated stations, foundation stations (placed on concrete foundation), truss stations (< 3×100 KVA), hanging stations (< 3×75 KVA), closed stations (installed indoors), complete stations (prefabricated houses). Depending on the cost and needs, we choose different types of transformers.
+ This is the most popular type of substation used today, suitable for construction and power supply in densely populated urban areas. It has a size that can be placed indoors, ensuring aesthetics and safety for people around. There are 2 types of indoor substations: closed substations and Gis substations.
+ Gis substation: is a substation that uses closed distribution equipment insulated with SF6 gas. The characteristic of this type of substation is that the construction area of the substation is about several dozen times smaller than that of an outdoor substation.
MST: 0319 105 825
 Số 64, Đường 52, Phường Cát Lái, TP. Hồ Chí Minh
Số 64, Đường 52, Phường Cát Lái, TP. Hồ Chí Minh
 0918 73 72 74
0918 73 72 74
 huynqthienviet@gmail.com
huynqthienviet@gmail.com
 www.thienvietvn.com
www.thienvietvn.com
Hotline
